1.定义一个自定义版本注解
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface ApiVersion { /** * @return版本号 */ int value( ) default 1; } 2.自定义URL匹配规则ApiVersionCondition
package com.yangjunbo.helloword.properties; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition.RequestCondition; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; /*接下来定义URL匹配逻辑,创建ApiVersionCondition类并继承RequestCondition接口, 其作用是进行版本号筛选,将提取请求URL中的版本号与注解上定义的版本号进行对比,以此来判断某个请求应落在哪个控制器上。*/ public class ApiVersionCondition implements RequestCondition<ApiVersionCondition> { private final static Pattern VERSION_PREFIX_PATTERN = Pattern.compile(".*v(\\d+).*"); private int apiVersion; ApiVersionCondition(int apiVersion) { this.apiVersion = apiVersion; } private int getApiVersion() { return apiVersion; } @Override public ApiVersionCondition combine(ApiVersionCondition apiVersionCondition) { return new ApiVersionCondition(apiVersionCondition.getApiVersion()); } @Override public ApiVersionCondition getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) { Matcher m = VERSION_PREFIX_PATTERN.matcher(httpServletRequest.getRequestURI()); if (m.find()) { Integer version = Integer.valueOf(m.group(1)); if (version >= this.apiVersion) { //apiVersion = version; return this; } } return null; } @Override public int compareTo(ApiVersionCondition apiVersionCondition, HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) { return apiVersionCondition.getApiVersion() - this.apiVersion; } } 3.使用RequestMappingHandlerMapping创建自定义的映射处理程序,根据Request参数匹配符合条件的处理程序
package com.yangjunbo.helloword.properties; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition.RequestCondition; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class ApiRequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingHandlerMapping { private static final String VERSION_FLAG = "{version}"; private static RequestCondition<ApiVersionCondition> createCondition(Class<?> clazz) { RequestMapping classRequestMapping = clazz.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class); if (classRequestMapping == null) { return null; } StringBuilder mappingUrlBuilder = new StringBuilder(); if (classRequestMapping.value().length > 0) { mappingUrlBuilder.append(classRequestMapping.value()[0]); } String mappingUrl = mappingUrlBuilder.toString(); if (!mappingUrl.contains(VERSION_FLAG)) { return null; } ApiVersion apiVersion = clazz.getAnnotation(ApiVersion.class); return apiVersion == null ? new ApiVersionCondition(1) : new ApiVersionCondition(apiVersion.value()); } @Override protected RequestCondition<?> getCustomMethodCondition(Method method) { return createCondition(method.getClass()); } @Override protected RequestCondition<?> getCustomTypeCondition(Class<?> handlerType) { return createCondition(handlerType); } } 4.配置注册自定义的RequestMappingHandlerMapping
package com.yangjunbo.helloword.properties; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcRegistrations; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping; @Configuration public class WebMvcRegistrationsConfig implements WebMvcRegistrations { @Override public RequestMappingHandlerMapping getRequestMappingHandlerMapping() { return new ApiRequestMappingHandlerMapping(); } } 5.创建测试接口
package com.yangjunbo.helloword.controller.v1; import com.yangjunbo.helloword.common.JSONResult; import com.yangjunbo.helloword.properties.ApiVersion; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; // V1 版本的接口定义 @RestController @RequestMapping("api/{version}/order") public class OrderV1Controller { @GetMapping("/delete/{orderId}") public JSONResult deleteOrderById(@PathVariable String orderId) { System.out.println("V1删除订单成功:"+orderId); return JSONResult.ok("V1删除订单成功"); } @GetMapping("/detail/{orderId}") public JSONResult queryOrderById(@PathVariable String orderId) { System.out.println("V1获取订单详情成功:"+orderId); return JSONResult.ok("V1获取订单详情成功"); } } package com.yangjunbo.helloword.controller.v2; import com.yangjunbo.helloword.common.JSONResult; import com.yangjunbo.helloword.properties.ApiVersion; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; // V2 版本的接口定义 @ApiVersion(2) @RestController @RequestMapping("api/{version}/order") public class OrderV2Controller { @GetMapping("/detail/{orderId}") public JSONResult queryOrdearById(@PathVariable String orderId) { System.out.println("V2获取订单详情成功:"+orderId); return JSONResult.ok("V2获取订单详情成功"); } @GetMapping("/list") public JSONResult list() { System.out.println("V2,新增list订单列表接口"); return JSONResult.ok(200,"V2,新增list订单列表接口"); } } 6.访问接口测试
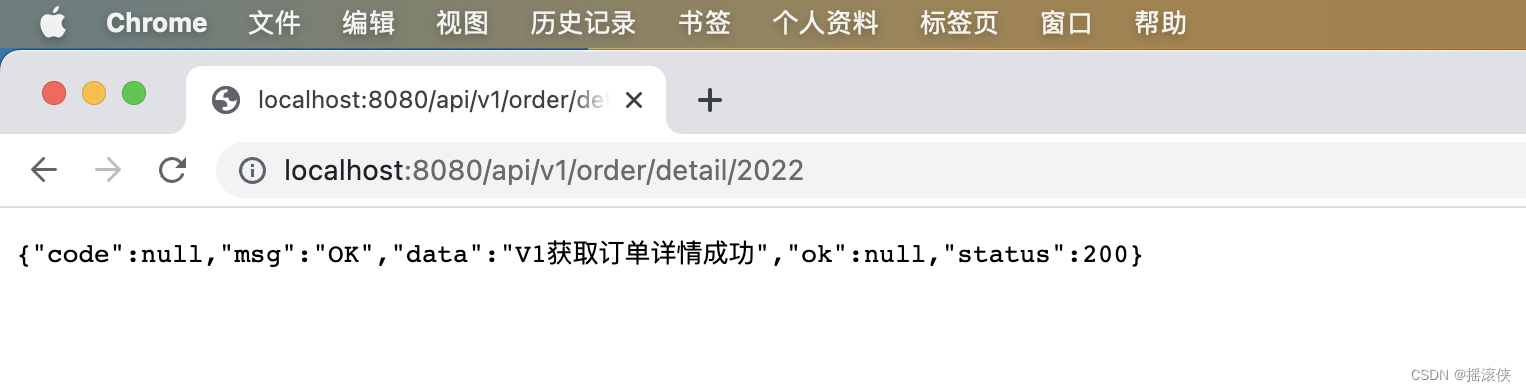
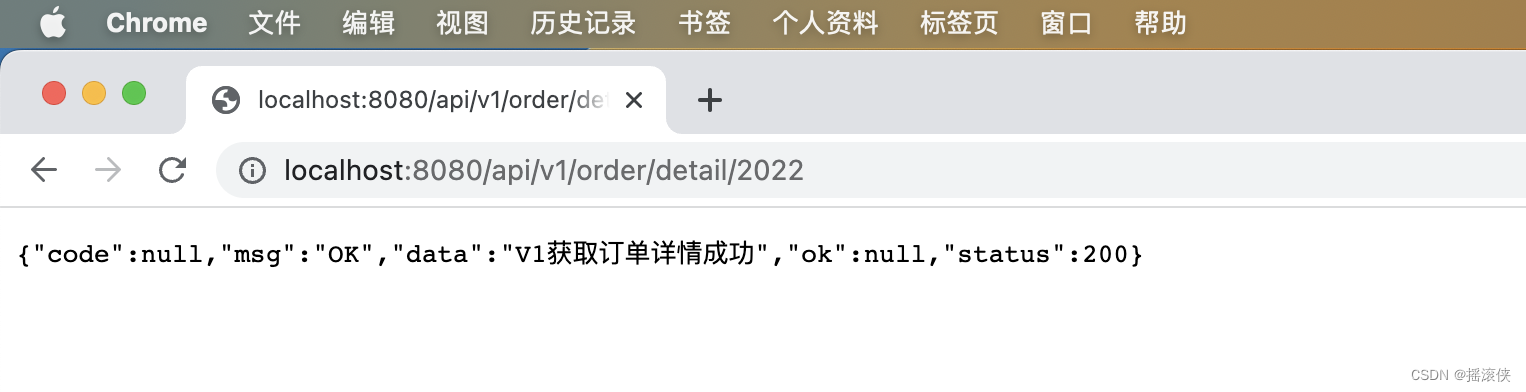
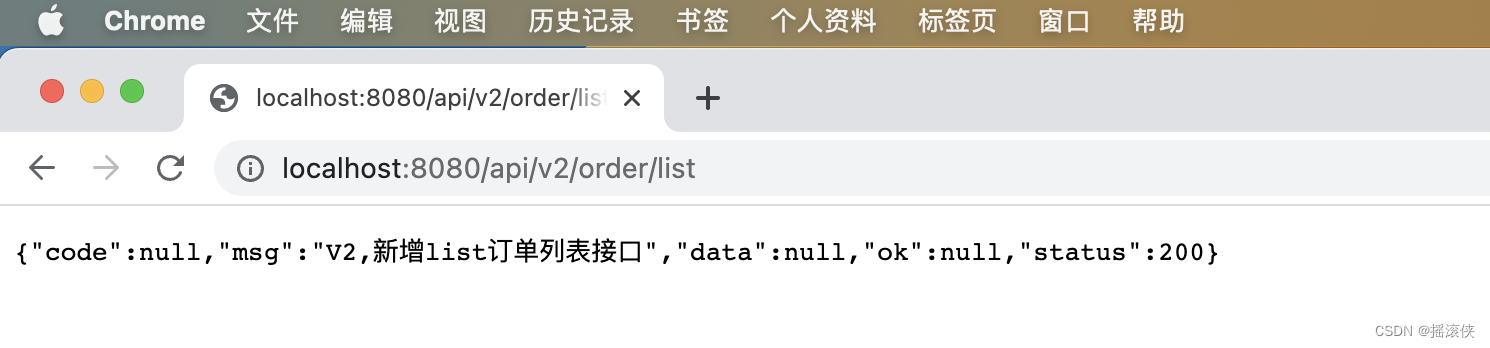
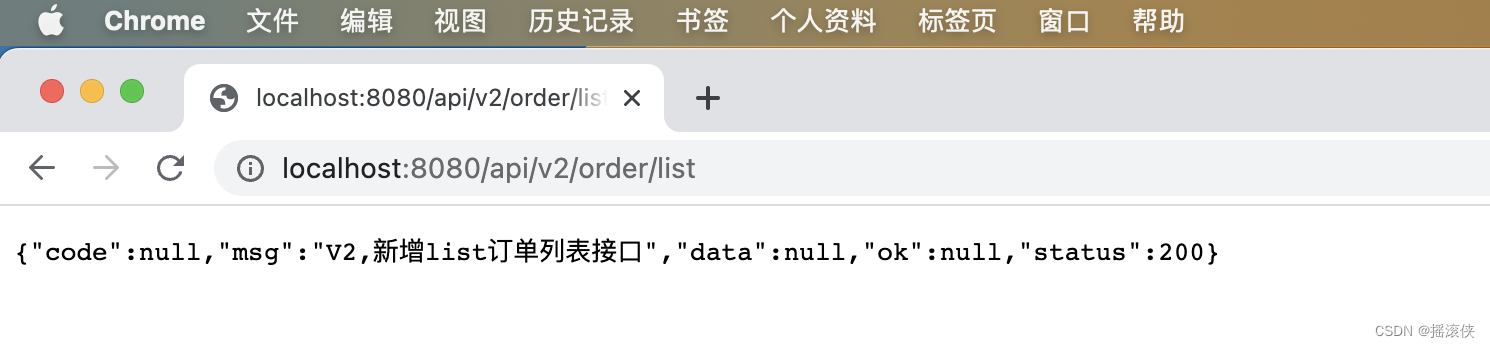
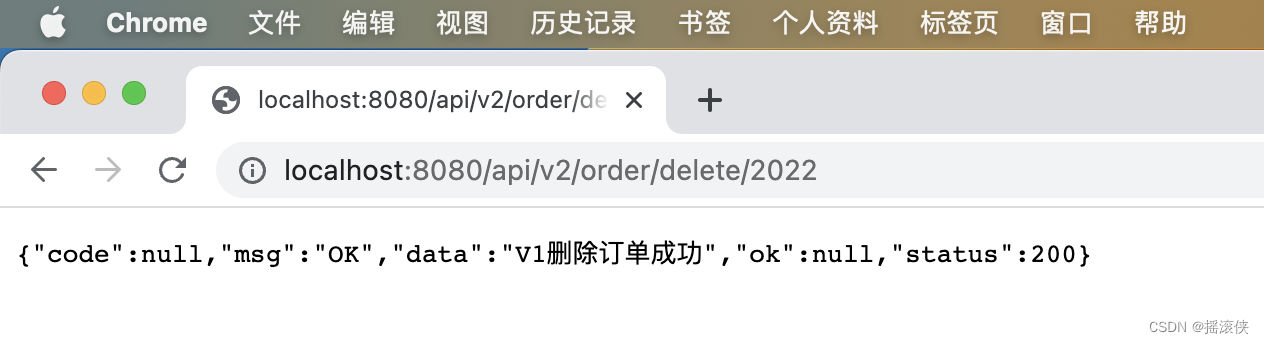
以上验证情况说明Web API的版本控制配置成功,实现了旧版本的稳定和新版本的更新。
1)当请求正确的版本地址时,会自动匹配版本的对应接口。
2)当请求的版本大于当前版本时,默认匹配最新的版本。
3)高版本会默认继承低版本的所有接口。实现版本升级只关注变化的部分,没有变化的部分会自动平滑升级,这就是所谓的版本继承。
4)高版本的接口的新增和修改不会影响低版本。
这些特性使得在升级接口时,原有接口不受影响,只关注变化的部分,没有变化的部分自动平滑升级。这样使得Web API更加简洁,这就是实现Web API版本控制的意义所在。
参考书籍 《springboot从入门到实战-章为忠著》
热门文章
- 动物能打疫苗吗有毒吗视频(动物打疫苗有什么作用)
- 动物医院的英语短语有哪些(动物医院英语怎么写)
- 动物医院诊疗范围有哪些项目呢(动物医院看病贵吗)
- 12月19日→22.7M/S|2024年最新免费节点BifrosTV订阅链接地址
- 11月6日→21.6M/S|2024年最新免费节点BifrosTV订阅链接地址
- 1月17日→22.8M/S|2025年最新免费节点BifrosTV订阅链接地址
- 11月27日→20.7M/S|2024年最新免费节点BifrosTV订阅链接地址
- netty系列之:netty中的核心MessageToByte编码器
- 猫咪不打疫苗就绝育(猫咪不打疫苗就绝育了)
- 天津市宠物领养机构电话(天津市宠物领养中心地址)